The nature/nurture debate that posits a competition between biological and social/cultural influences on human behavior is alive and well in the mass media. But scholars largely agree that culture and biology interact; biological realities shape our social world, but our social world also shapes our biologies.
One strain of research demonstrating this has shown that men’s testosterone levels (associated with feelings of well-being) rise and drop in response to social (and socially constructed) cues. For example, the testosterone levels of the winner of a tennis match will rise after his win, while his opponent will see his levels go down. Similarly, measuring men’s testosterone levels won’t tell you which men walking down the sidewalk will enter a strip club, but the men leaving the strip club will have higher testosterone levels than the men who passed it by.
Matt C. alerted me to a test of this phenomenon using the Presidential election. There was a slight drop in testosterone levels for men who voted for Obama (normal because men’s testosterone levels tend to drop at night), but a dramatic drop for men who voted for McCain or the Libertarian candidate, Barr.
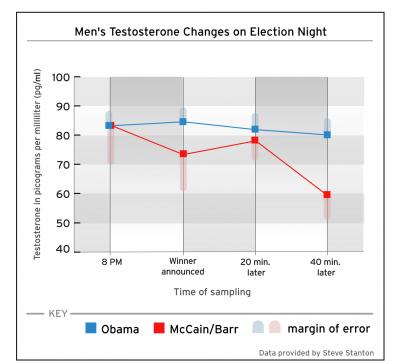
So, there you have it, biological responses to social cues.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.

Comments 20
Fernando — October 27, 2009
Just like by seeing an attractive naked woman my body's blood flow will change. Point is, yes, social influence biology all the time in unsurprising ways. What I find interesting though is the separation between social and biology. Why can't we put it all together in one package that attempts to describe human behavior? Extreme heat, cold, a virus, other non social things also change our behavior. I think it should be just about how outside stimulis interact with innate tendencies, not how certain field affects another.
George — October 27, 2009
I don't think this is exactly what is meant by the nature/nurture debate. That people are physiologically affected by outside events is well understood. When you experience stimuli of some kind the chemical balance of your body changes. Another example is when you get stressed out your stomach hurts, because there's some hormone released (seratonin?) that interferes with digestion.
The nature/nurture debate is about how much of human behaviour, both psychological and sociological, depends on human evolution and how much on individual experiences. For example, there's a lot of discussion on this blog about gender roles. I think it's fair to say that the perspective of most of those posts is that such behaviour is learned. A nature perspective would say that humans have evolved certain gender roles through natural selection.
The nature arguments are potentially very powerful. It is possible that much of human behaviour, including such high level phenomena as social interactions and economics could eventually be understood biologically. Many people have argued that the social sciences should actually try to move closer to this more scientific approach. See for example Edward Wilson's book "Consilience".
KD — October 27, 2009
I think it's important to keep in mind that:
1) Similar studies have shown that women's testosterone levels also rise and fall depending on the outcome of competition.
2) The change in horomones that studies like this one shows are generally small and insignificant.
3) There are a lot of common misconceptions about testosterone and what it does. It does not cause aggression, for example, it only exaggerates aggression that might already exist. Actually, estrogen has a stronger direct correlation to aggression.
While studies like this might lead to insight, the danger of trying to use biology to explain behavior is that most people doing so are trying to justify existing inequality and are willing to overlook good data that suggests alternative explanations to support the opinions they already hold.
Beelzebub — October 27, 2009
Did McCain's male voters experience a drop in testosterone because he lost or did McCain lose because his male voters were going to experience a drop in testosterone later in the night? The world may never know...
Jeremiah — October 28, 2009
It would be interesting to see if any correlations pop up when scaled over time. For instance, do men who experience longer series of "ups" behave differently than those who experience long series of "downs?" Are these connected to manic depression?
Does a long series of "ups" correlate with higher self-confidence or perceived attractiveness by potential mates?
Bekki — October 28, 2009
I think that when we try to make sense of biological and social influences on human beings it's important to consider human development itself.
The field of Biology is very relevant when we are studying animal development and their behavior. But there are distinct differences in human development; A concept that Berger and Luckmann in "The Social Construction of Reality" use to contrast humans and animals is "exterogestation", basically referring to how the fetal period in humans actually extends through the first year of birth. For animals, important organismic developments are completed within the mother's womb, but for the human infant these developments are completed after it's separation from mother's womb. The human infant is still developing biologically in the context of its environment--thus the process of becoming "human" involves not only a relationship with the natural environment, but with the specific cultural and social order one is born into.
In Barbara Rogoff's terms humans are "biologically culture" (e.g. humans are born with the potential for language acquisition).
Biology and Sociology are intertwined in this respect. Which is why Nature/Nurture are not opposed to each other, but involve an interrelationship. The rivalry really is just a challenge from the Nurture side reminding us "Hey! Don't disregard me!" Because we tend to "naturalize" social phenomena (What is normal, is seen as natural) it downplays the important role that context has on our experience as humans.
Daniel — October 31, 2009
"So, there you have it, biological responses to social cues."
What you also have are some pretty hefty error bars in the McCain/Barr measurements. I'm not disputing the findings or the idea that society can influence biology--it's still a quite interesting study too. I just would like to point out that what appears to be a huge drop in the testosterone levels in that group also contains a big error margin. The difference may not actually be as drastic as it appears.
Michelle — November 9, 2009
I would love to see a study to show how the social world shapes female attitudes toward their own sexuality. They say that testosterone goes up and down in certain social contexts, such as a man leaving a strip club. Do women's hormone levels change as well in a certain sexual context? I am older and have seen women's sexual attitudes change quite a lot over the last twenty years. More today than ever, Pop culture, advertising, and fashion has been sexualizing women disproportionately in comparison to men, while men are being desexualized. Women wear less and less, while men cover up more and more. Long baggy shorts, long baggy swimsuits, all in an attempt to showcase only women and hide the male physique. Could all of this socialization be giving the message to women that they should find the male form distasteful, something that should be hidden and covered up? While all of this is going on, women often say, they don't like to see a man at all from the waist down. And suddenly anything above the knee is unattractive on a men. When I was younger, men wore shorter shorts, and short swim trunks and no one gave them any grief over it. They were not laughed at, and they were not considered gay. It was considered attractive and sexy. Not so today. Women are changing their attitude toward the male form. Lesbianism is becoming more mainstream, and women are expected to feel cool about it. I keep hearing how European women are far more appreciative of the sexual attractiveness of men, and like to view the male physique. American women seem to be getting less interested in seeing men as sexual images, but embrace women as such. Something about this seems a bit odd to me. Could it be that our American society is molding a whole new attitude toward the sexuality of men onto American women? Could these sociological pressures actually be facilitating a slight change on the biology of women in America?