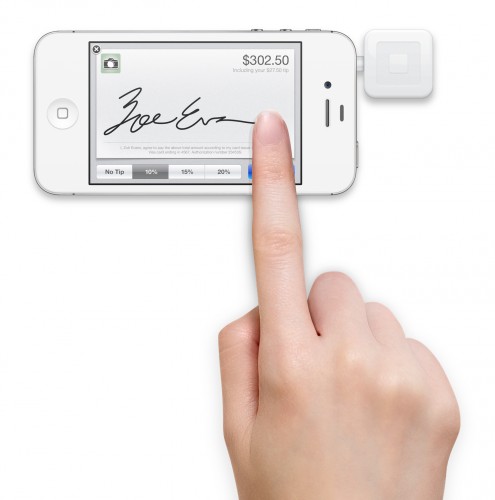
The Pew Internet and American Life Project and researchers from Elon University asked over a thousand “experts” about the future of money. Specifically, they were interested in the potential replacement of cash and credit/debit cards with smart-device technologies.
The majority of respondents (65%) believe that smartphones will largely replace cash and credit/debit cards by the year 2020. Others, however, believe that our infrastructure is too closely tied with a cash/card based system to be fully replaced. Further, most experts note that not ALL consumers will make the switch, as some will resist over concerns about privacy and anonymity. Finally, many predict that adoption will differ across demographics (with younger consumers replacing cash/credit at a faster rate than older consumers). Read the full report here.
Indeed, it is not difficult to imagine a largely smart-device based currency system—as this is already prevalent in Japan and growing in the U.S.. The next step is to imagine the social implications of such a system. I believe that these implications will be twofold: First, we will become more efficient consumers. Second, identity and practices of consumption will be more explicitly and directly linked—solidifying the connection between self and stuff. more...