 News stories of officers being attacked and killed while in the line of duty have become regular features of the nightly news broadcast, but does this increase in coverage reflect an increase in reality? My analysis suggests no.
News stories of officers being attacked and killed while in the line of duty have become regular features of the nightly news broadcast, but does this increase in coverage reflect an increase in reality? My analysis suggests no.
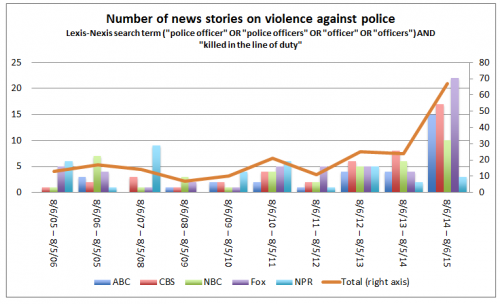
A count of stories of police officers killed in the line of duty shows that media attention to these killings has increased dramatically since the death of Michael Brown in Ferguson, Missouri. Between one third and one half of all of the news stories that the “legacy” networks’ (ABC, CBS, NBC) have done on this topic over the last ten years have appeared in the last year. Fox News has run more stories on this topic this year than it did over the four previous years combined.
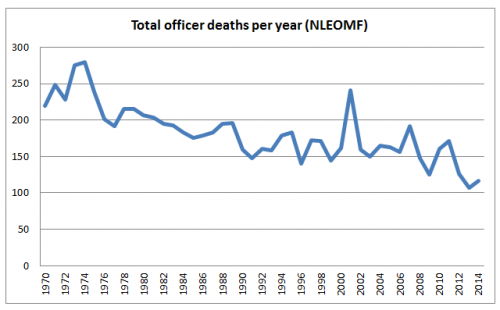
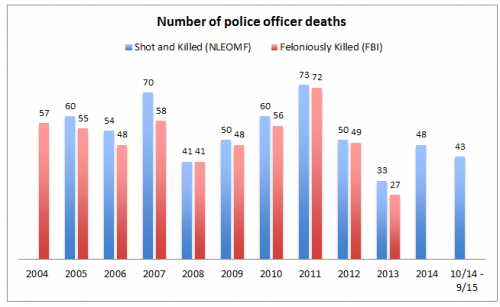
 Actual incidences of fatal violence against police officers perpetrated by civilians, however, have not been on the rise. Data on police officer deaths compiled by the FBI and the National Law Enforcement Memorial Fund shows that the year since Michael Brown’s death has not been especially dangerous for police officers, at least when it comes to the danger of being maliciously attacked by another person. According to the National Law Enforcement Memorial Fund’s data, in the year following Michael Brown’s death, 43 police officers were shot and killed, which is significantly less than the average of 54 police officer shooting per year over the last ten years. Looking back even further, policing is much safer now than any time in the last 45 years.
Actual incidences of fatal violence against police officers perpetrated by civilians, however, have not been on the rise. Data on police officer deaths compiled by the FBI and the National Law Enforcement Memorial Fund shows that the year since Michael Brown’s death has not been especially dangerous for police officers, at least when it comes to the danger of being maliciously attacked by another person. According to the National Law Enforcement Memorial Fund’s data, in the year following Michael Brown’s death, 43 police officers were shot and killed, which is significantly less than the average of 54 police officer shooting per year over the last ten years. Looking back even further, policing is much safer now than any time in the last 45 years.
The impression that civilians are targeting officers, then, is a reflection of media coverage, not reality. This is a phenomenon called agenda setting, a process by which the media put an item on the public agenda.
What’s particularly troubling here is not necessarily that the media has put police killings by civilians on the agenda, but that they have failed to do so when it was. Many more officers were being killed in the line of duty in 2011, the most lethal year for police officers over the last ten years, and yet the news media gave scant attention to their deaths.
What explains this divergence between the reality of violence against police officers and the degree to which the news media covers it? It is not simply a matter of ideology. Fox News — the most conservative of the news outlets shown here — has run more stories on police officer deaths this year than the other news outlets, but we can see the same basic pattern across all news outlets, with the exception of National Public Radio.
I suspect that the answer has to do with news framing and the way in which news organizations display their objectivity by giving equal time to “both sides of the story.” Faced with questions and criticism after each high-profile event of police violence against civilians, police spokespeople constantly remind us of the dangers faced by their officers as a means of blunting those criticisms. In giving equal airtime to “both sides” of the issue, news outlets help to spread this message. Whether out of an internal desire to be “balanced” or in direct response to these PR moves, media has picked up the “dangers of policing” narrative.
Ironically, in their effort to tell a balanced story, the news media has interjected itself in a contentious debate by presenting a false symmetry of violence when, in reality, the newsworthy trend is the dramatic increase in deaths at the hands of police.
This narrative is not only bad for understanding what’s really happening between police officers and civilians, it may also be bad for police officers themselves by distracting us from the more common sources of police officer death. As the National Law Enforcement Memorial Fund notes, over the last three years the leading cause of police officer deaths in the line duty is car accidents. Indeed, while the number of officers shot and killed is lower this year than for the same time period last year, the total number of officers killed is higher, and that is due to the much higher number of officers killed in accidents.
The news media would contribute much more to the important conversation about the relationship between civilians and police if they were more honest about the relative rates of harm from each to the other.
Aaron Major, PhD is an associate professor of sociology at the University at Albany – SUNY. He does research in the areas of globalization and economic policy, neoliberalism and public policy, and social inequality.

Comments 9
Umlud — September 14, 2015
An additional point is, of course, the increasing visibility of civilians being shot at, beaten, or pepper-sprayed, tazed, and/or illegally detained by police.
The increasing presence and proliferation of videos (even more than photos) of police over-reaction and escalation of encounters with civilians is making the police (as an institution) act very human in "circling the wagons" and (effectively) preferring to protect their own (even when "their own" includes poor examples of police officers that they might otherwise wish were gone). Even though this human response is ultimately counterproductive, since it tends to magnify the "us" vs "them" binary mindset...
Bill R — September 15, 2015
It is equally likely that the media is reporting more now on murders of police because of the interest among their customers in stories of murders INVOLVING police in general. The media might have simply latched onto a storyline that sells and will milk it to death from every angle, like they do with all stories that grab attention.
Your comment about media balancing the issue by giving time to "both sides" unnecessarily pits police against citizens as natural enemies. I understand you're trying to cast the police in a negative light but you're playing games with logic in the process.
PigStateNews — September 18, 2015
At least 851 people have been killed by U.S. police since January 1, 2015.
At least 1,106 were killed in 2014.
At least 2,725 have been killed since May 1, 2013.
killedbypolice.net
Several times as many have been shot and survived, initially.
An untold number have been tortured, brutalized, caged, raped and molested.
Jim Wiseman — October 2, 2015
I understand why you would refer to non-LEOs as "civilians" for purposes of discussion, but please don't. That just adds to the "us against them" mentality of police, who are citizens as well.
Media spin on violence against police - Treat Them Better — October 24, 2015
[…] Media spin on violence against police […]