Cross-posted at Chris Uggen’s Blog.
I’ve been reluctant to write about the terrible events at Sandy Hook Elementary School because the wounds are still too fresh for any kind of dispassionate analysis. As a social scientist, however, I’m disappointed by the fear-mongering and selective presentations of the research evidence I’ve read in reports and op-eds about Friday’s awful killing.
Such events could help move us toward constructive actions that will result in a safer and more just world — or they could push us toward counter-productive and costly actions that simply respond to the particulars of the last horrific event. I will make the case that a narrow focus on stopping mass shootings is less likely to produce beneficial changes than a broader-based effort to reduce homicide and other violence. We can and should take steps to prevent mass shootings, of course, but these rare and terrible crimes are like rare and terrible diseases — and a strategy to address them is best considered within the context of more common and deadlier threats to population health. Five points:
1. The focus on mass shootings obscures over 99 percent of homicide victims and offenders in the United States.
The numbers should not matter to parents who must bury their children, but they are important if policy makers are truly committed to reducing violent deaths. There are typically about 25 mass shootings and 100 victims each year in the United States (and, despite headlines to the contrary, mass shootings have not increased over the past twenty years). These are high numbers by international standards, but they pale relative to the total number of killings – about 14,612 victims and 14,548 offenders in 2011. In recent years, the mass shooters have represented less than two-tenths of 1 percent of the total offenders, while the victims have represented less than one percent of the total homicide victims in any given year. We are understandably moved by the innocence of the Sandy Hook children, but we should also be moved by scores of other victims who are no less innocent. There were 646 murder victims aged 12 or younger in the United States in 2011 alone — far more than all the adults and children that died as a result of mass shootings.
2. The focus on mass shootings leads to unproductive arguments about whether imposing sensible gun controls would have deterred the undeterrable.
As gun advocates are quick to point out, many of the perpetrators in mass shootings had no “disqualifying” history of crime or mental disorder that would have prevented them from obtaining weapons. And, the most highly motivated offenders are often able to secure weapons illegally. Even if such actions do little to stop mass shootings, however, implementing common-sense controls such as “turning off the faucet” on high capacity assault weapons, tightening up background checks, and closely monitoring sales at gun shows are prudent public policy. But the vast majority of firearms used in murders are simple handguns. I would expect the no-brainer controls mentioned above to have a modest but meaningful effect, but we will need to go farther to have anything more than an incremental effect on mass shootings and gun violence more generally.
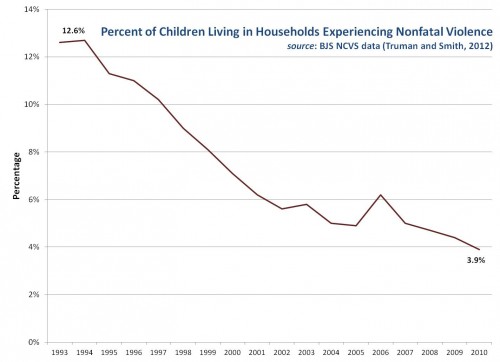
3. The focus on mass shootings obscures the real progress made in reducing the high rates of violence in the United States.
I heard one commentator suggest that America had finally “hit bottom” regarding violence. Well, this is true in a sense — we actually hit bottom twenty years ago. The United States remains a violent nation, but we are far less violent today than we were in the early 1990s. Homicide rates have dropped by 60 percent and the percentage of children annually exposed to violence in their households has fallen by 69 percent since 1993:
We can and should do better, of course, but these are not the worst of times.
4. The focus on mass shootings exaggerates the relatively modest correlation between mental illness and violence.
Those who plan and execute mass shootings may indeed have severe mental health problems, though it is difficult to say much more with certainty or specificity because of the small number of cases in which a shooter survives to be examined. We do know, however, that the correlation between severe mental illness and more common forms of violence is much lower — and that many types of mental health problems are not associated with violence at all.
5. The focus on mass shootings leads to high-security solutions of questionable efficacy.
Any parent who has attempted to drop off a kid’s backpack knows that security measures are well in place in many schools. Rates of school crime continue to fall, such that schools are today among the safest places for children to spend so many of their waking hours. In 2008-2009, for example, only 17 of the 1,579 homicides of youth ages 5-18 occurred when students were at school, on the way to school, or at school-associated events. Of course we want to eliminate any possibility of children being hurt or killed at school, but even a 2 percent reduction in child homicide victimization outside of schools would save more lives than a 90 percent reduction in school-associated child homicide victimization. While every school must plan for terrible disasters in hopes that such plans will never be implemented, outsized investments in security personnel and technology are unlikely to serve our schools or our kids.
In the aftermath of so many deaths I am neither so cynical as to suggest that nothing will change nor so idealistic as to suggest that radical reform is imminent. I’m just hoping that the policy moves we make will address our all-too-common horrors as well as the rare and terrible events of the past week.
—————————
Chris Uggen is a professor of sociology at the University of Minnesota and the author of Locked Out: Felon Disenfranchisement and American Democracy, with Jeff Manza. You can follow him at his blog and on twitter.

Comments 57
Guest — December 21, 2012
Why do you keep posting this stuff? It's really insensitive to the victims and their families.
Yrro Simyarin — December 21, 2012
This is, far and away, the best thing I have read on this blog on this issue.
Jeff Pettorino — December 21, 2012
An outstanding analysis of the problem. We need to address these issues. All parties, gun advocates, gun control lobbyists, parents, politicians...but we need to do it without emotional the turmoil that these tragedies cause. Thanks for putting this together. It is a great piece that I will be sharing with everyone I know.
tree — December 21, 2012
And that people who suffer from mental illness are much more likely to be the victims of violence than the perpetrators.
The Gun Control Debate | Erin V Echols — December 21, 2012
[...] make the headlines, the focus of mass shooting actually obscures 99% of gun violence in the US. “In recent years, the mass shooters have represented less than two-tenths of 1 percent of the ... These issues matter significantly for how we construct policy to deal with gun [...]
myblackfriendsays — December 21, 2012
Thank you for posting this. An intelligent, measured and rational piece of writing in response to a horrible tragedy.
Frida — December 21, 2012
Why can't I reply to the most recent comment? It looks as if I am being censored. Anyway, I take it you also oppose the death penalty? Would this still be the case if your loved one had been raped and murdered by a dead-eyed megalomaniac serial killer?
A W — December 21, 2012
Holy cow, you're not complaining or nitpicking or pontificating hypotheticals. It's a holiday miracle!
A W — December 21, 2012
Dammit Disqus, that was a reply to @google-0701efaaf6f3d137dd427f9ef68f6beb:disqus. Can't even edit or reply to myself. grumblegrumble
A W — December 21, 2012
@Frida http://www.thinkingautismguide.com/2012/12/a-plea-from-scariest-kid-on-block.html
J E — December 21, 2012
Yo Erational, you cant just say noone deserves to die as if its absolute fact. Thats pretty subjective. I thought sociology types were above this sorta thing.
A W — December 21, 2012
@Frida No, I'm far more afraid of your ableism, seeing as I'm one of those 'dangerous creeps'. Someone like you is far more likely to commit violence against someone like me than the other way around.
A W — December 21, 2012
@Frida How ironic.
A W — December 21, 2012
The commenting system seems to be posting comments wherever it wants.
More on mental illness and violence:
http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/health-17182626
William Angel — December 21, 2012
David Hemenway, a Harvard professor of health policy and director of the Harvard Injury Control Research Center, told The New York Times, "Children ages 5 to 14 in the United States are 13 times as likely to be killed with guns as children in other industrialized countries "
Is that because of differences in gun control, differences in health care systems, or could it be socio-economic factors?
And if all three factors come into play which factor do you think is the most important?
A W — December 21, 2012
How DARE someone accuse you of being prone to violence, but it's perfectly acceptable to accuse people like me of the same thing. Anyone who thinks we're not dangerous is DELUDED and putting themselves at risk by being anywhere near someone like me.
When, in fact, people like you are more likely to commit violence against people like me.
Ironic.
Oldguy — December 22, 2012
This is like the way the media hypes plane crashes, while ignoring auto crash deaths. Everyone in this country is talking about 28 dead, but over 500 people have been shot this year in Chicago alone. Everyone who reads this- please give some serious thought to how the media leads and manipulates what we pay attention to.
Now think about what else they have led us to believe...
random — December 22, 2012
My perspective on these mass shootings...The Left's Failure Post-Newtown, ConnecticutWhat is the root cause of this tragedy and why isn't the Left talking about it?The reaction to the Connecticut killings demonstrates the need for the Western Left to reevaluate itself, and to remember that it was once a potent force, in order to become one again.http://alexfelipe.wordpress.com/2012/12/22/the-lefts-failure-post-newtown-connecticut/
Transreductionist — December 24, 2012
From the Associated Press Homepage: "The horrific massacre of 26 children and staff at a Connecticut elementary school, along with other mass shootings, was the top news story of 2012, narrowly edging out the U.S. election, according to the AP's annual poll of U.S. editors."
Make no mistake that the Sandy Hook mass killing functions within our society, and the subsequent politicization of the event points to much deeper problems as we bury our heads in the sand with such outrage.
Yesterday 14,000 children under the age of 5 died from under-nutrition (UNICEF data). Today 14,0000 more died. Tomorrow another 14,000 will die. Why is this not the most important story? I guess it is because here we can only hold ourselves accountable. Of course that is not much fun.
Of course Adam Lanza can not shoulder our problems by himself, and so we will support him in his gradual acceptance for the responsibility of his crime.
guest — January 17, 2013
great article. Excellent articulation of facts around a delicate emotional issue. Your only error was the comment on "common-sense controls such as “turning off the faucet” on high capacity assault weapons, tightening up background checks, and closely monitoring sales at gun shows" "expect the no-brainer controls mentioned above to have a modest but meaningful effect"
If you would have applied the same factual research to these comments you would quickly see how much in error they are. If the Sandy Hook shooter had a 10 round magazine instead of 30, would the first-graders have rushed him while he was reloading? Would the results have been any different if he used a shotgun or hunting rifle rather than the Bushmaster (which was one of the smallest calibers available)? How many of the mass shooting perps got their guns through the 'gun show loophole'?
Still a very worthwhile write-up, and thanks again for putting it out there.
The Truth About Violence and Gun Policy in the United States - — April 16, 2013
[...] post originally appeared on Sociological Images, a Pacific Standard partner [...]
A Letter to Students About School Gun Violence – Munson 4 East Penn Schools — October 23, 2019
[…] The Truth about Violence and Gun Policy in the U.S. […]