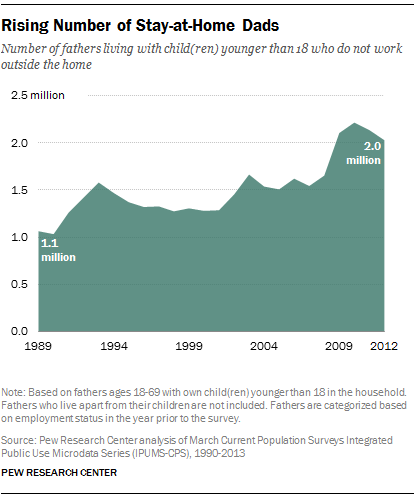
At Pew Social Trends, Gretchen Livingston has a new report on fathers staying at home with their kids. They define stay at home fathers as any father ages 18-69 living with his children who did not work for pay in the previous year (regardless of marital status or the employment status of others in the household). That produces this trend:
At least for the 1990s and early-2000s recessions, the figure very nicely shows spikes upward of stay-at-home dads during recessions, followed by declines that don’t wipe out the whole gain — we don’t know what will happen in the current decline as men’s employment rates rise.
In Pew’s numbers 21% of the stay at home fathers report their reason for being out of the labor force was caring for their home and family; 23% couldn’t find work, 35% couldn’t work because of health problems, and 22% were in school or retired.
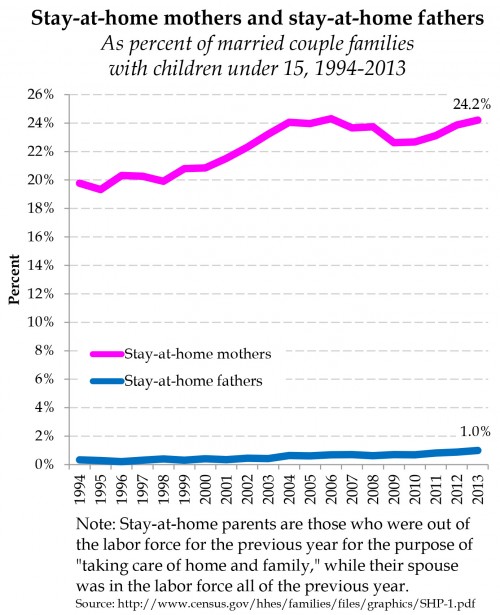
It is reasonable to call a father staying at home with his kids a stay at home father, regardless of his reason. We never needed stay at home mothers to pass some motive-based criteria before we defined them as staying at home. And yet there is a tendency (not evidenced in this report) to read into this a bigger change in gender dynamics than there is. The Census Bureau has for years calculated a much more rigid definition that only applied to married parents of kids under 15: those out of the labor force all year, whose spouse was in the labor force all year, and who specified their reason as taking care of home and family. You can think of this as the hardcore stay at home parents, the ones who do it long term, and have a carework motivation for doing it. When you do it that way, stay at home mothers outnumber stay at home fathers 100-to-1.
I updated a figure from an earlier post for Bryce Covert at Think Progress, who wrote a nice piece with a lot of links on the gender division of labor. This shows the percentage of all married-couple families with kids under 15 who have one of the hardcore stay at home parents:
That is a real upward trend for stay at home fathers, but that pattern remains very rare.
See the Census spreadsheet for yourself here. Cross-posted at Pacific Standard.
Philip N. Cohen is a professor of sociology at the University of Maryland, College Park, and writes the blog Family Inequality. You can follow him on Twitter or Facebook.