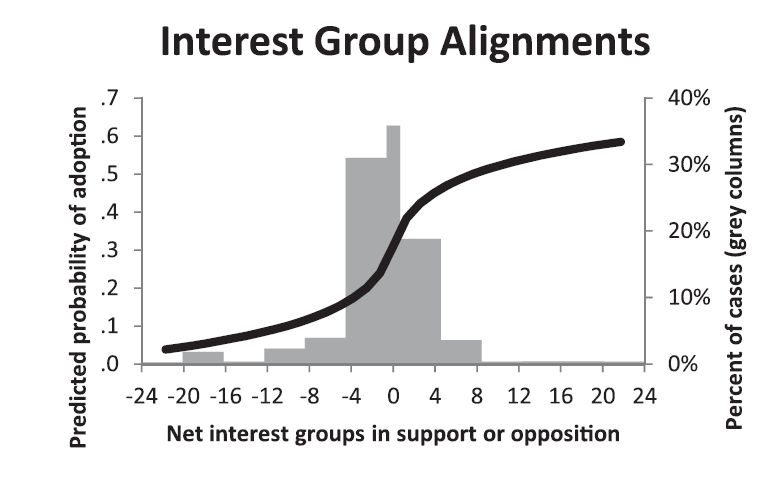
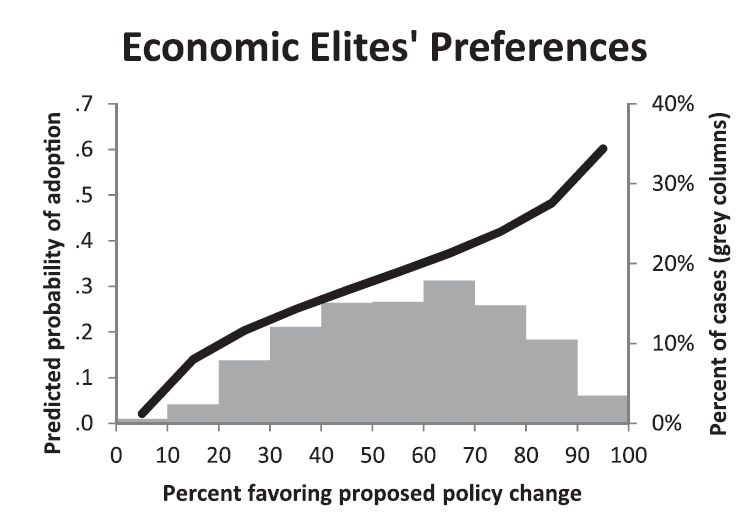
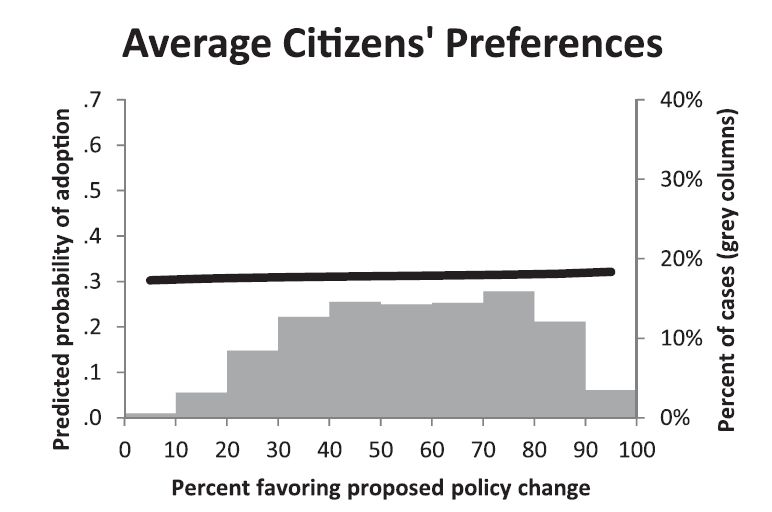
Police brutality is a problem in US criminal justice. Police-worn body cameras are one potential “remedy” to these violent encounters, but they have both benefits and drawbacks. The cameras may increase transparency and improve police legitimacy, promote legally compliant behavior among both police officers and citizens; enhance evidence quality that can improve resulting legal proceedings; and deter officers’ use-of-force. Conversely, body-worn cameras could create privacy concerns for the officer and the citizenry and place a large logistical and financial burden on already cash-strapped law enforcement agencies.
.
This issue is so timely that research is only now starting to see publication, but we do have some early insights. The first observational studies examining the use of police-worn body cameras were carried out in England and Scotland. They found rates of citizen complaints dropped after body cameras were introduced. Preliminary results from an experimental study in Phoenix, Arizona also suggest that the use of body cameras reduces both self-reported and official records of citizen complaints.
The first experimental evidence concerning use-of-force comes from a large study in the Rialto, California Police Department, and the results should encourage advocates of body cameras. The study randomly assigned particular police shifts to wear body cameras (the “treatment”). Police shifts in the treatment condition are associated with reduced use-of-force and citizen complaints against the police were significantly reduced. Shifts in the control condition, in contrast, saw roughly twice as much use-of-force as the treatment condition.
The research so far suggests that body cameras are a promising way to reduce unnecessary use of force.
Ryan Larson is a graduate student studying the sociology of crime at the University of Minnesota. His research interests extend to statistics, sport, and media. He writes for and is on the Graduate Editorial Board of The Society Pages. This post originally appeared at There’s Research on That!