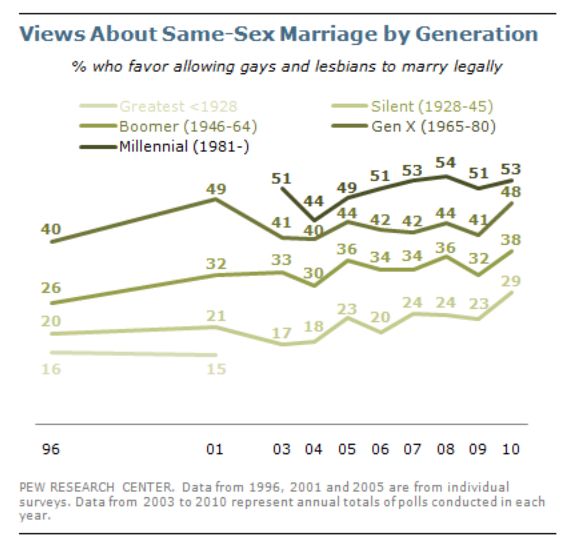
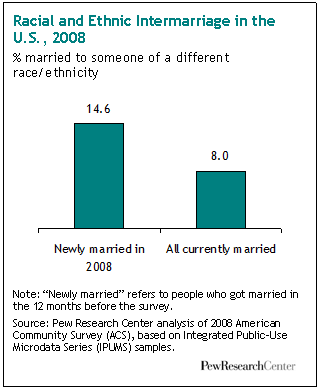
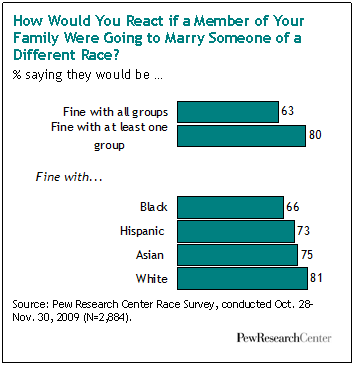
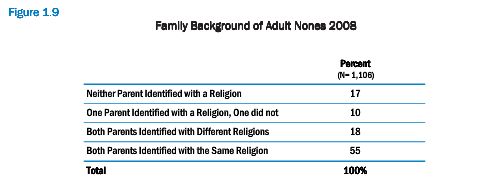
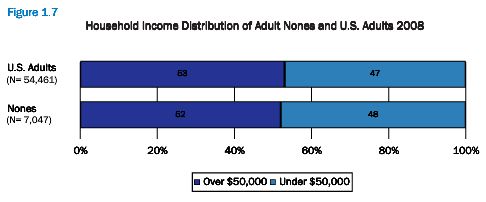
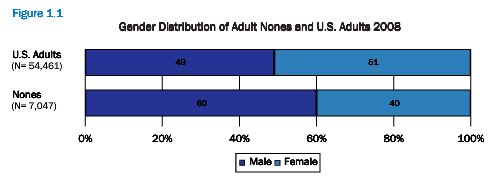
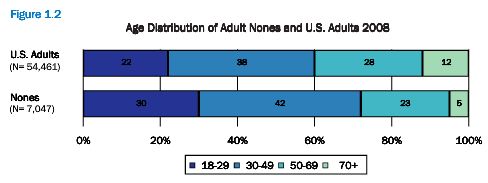
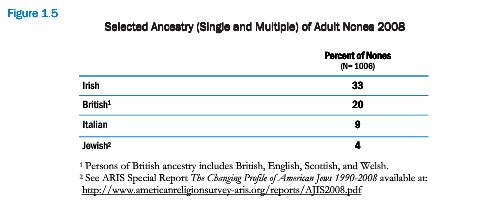
Cross-posted at Montclair SocioBlog.
We’ve known for a long time that surveys are often very bad at predicting behavior. To take the example that Malcom Gladwell uses, if you ask Americans what kind of coffee they want, most will say “a dark, rich, hearty roast.” But what they actually prefer to drink is “milky, weak coffee.”
Something that sounds good in the abstract turnsout to be different from the stuff you actually have to drink.
Election polls usually have better luck since indicating your choice to a voting machine isn’t all that different from speaking that choice to a pollster. But political preference polls as well can run into that abstract-vs.-actual problem.
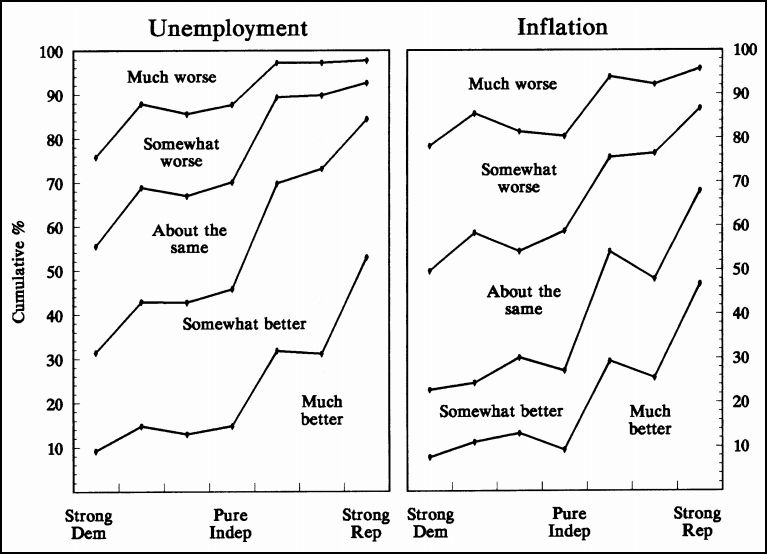
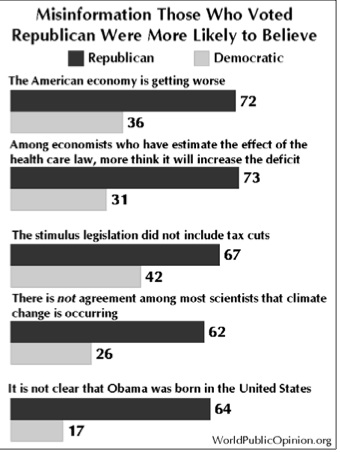
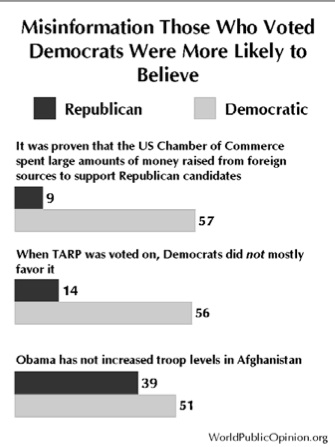
Real Clear Politics recently printed some poll results that were anything but real clear. RCP looked at polls matching Obama against the various Republican candidates. In every case, if you use the average results of the different polls, Obama comes out on top. But in polls that matched Obama against “a Republican,” the Republican wins.
The graph shows only the average of the polls. RCP also provides the results of the various polls (CNN, Rasmussen, ABCl, etc.)
Apparently, the best strategy for the GOP is nominate a candidate but not tell anyone who it is.