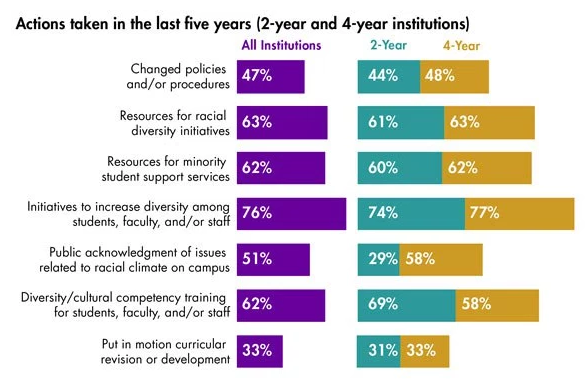
“[A]n analysis of traffic can enrich sociological theory.” (Schmidt-Relenberg, 1968: 121)
Almost everywhere we go is a “gendered space.” Although men and women both go to grocery stores, different days of the week and times of the day are associated with different gender compositions of shoppers. Most of our jobs are gendered spaces. In fact, Census data show that roughly 30% of the 66,000,000 women in the U.S. labor force occupy only 10 of the 503 listed occupations on the U.S. Census. You’d probably be able to guess what some of these jobs are just as easily as you might be able to guess some of the very few Fortune 500 companies have women CEOs. Sociologists refer to this phenomenon as occupational segregation, and it’s nothing new. Recently, I did read about a gender segregated space that is new (at least to me): traffic.

When I picture traffic in my head, I think of grumpy men driving to jobs they hate, but this is misleading. Women actually make up the vast majority of congestion on the roads. One way of looking at this is to argue that women are causing more congestion on our roads. But another way to talk about this issue (and the way to talk about this issue that is consistent with actual research) is to say that women endure more congestion on the roads.
Women were actually the first market for household automobiles in the U.S. Men generally traveled to work by public transportation. Cars sold to households were marketed to women for daily errands. This is why, for instance, early automobiles had fancy radiator caps with things like wings, angels and goddesses on them. These were thought to appeal to women’s more fanciful desires.
Traffic increased a great deal when women moved into the labor force. But this is not exactly what accounts for the gender gap. In the 1950s, car trips that were work-related accounted for about 40% of all car use. Today that number is less than 16%. The vast majority of car trips are made for various errands: taking children to school, picking up groceries, eating out, going to or from day care, shopping, and more shopping. And it’s women who are making most of these trips. It’s a less acknowledged portion of the “second shift” which typically highlights women’s disproportionate contribution to the division of labor inside the household even when they are working outside of the household as well.
Traffic research has shown that women are more than two times more likely than men to be taking someone else where they need to go when driving. Men are more likely to be driving themselves somewhere. Women are also much more likely to string other errands onto the trips in which they are driving themselves somewhere (like stopping at the grocery store on the drive home, going to day care on the way to work, etc.). Traffic experts call this “trip chaining,” but the rest of us call it multi-tasking. What’s more, we also know that women, on average, leave just a bit later than men do for work, and as a result, are much more likely to be making those longer (and more involved) trips right in the middle of peak hours for traffic.
Who knew? It’s an under-acknowledged gendered space that deserves more attention (at least from sociologists). Traffic is awful, and if we count up all that extra time and add it to the second shift calculations made by Arlie Hochschild, I think we have a new form of inequality to complain about.
Tristan Bridges, PhD is a sociologist at the College at Brockport (SUNY). With CJ Pascoe, he is the editor of Exploring Masculinities: Identity, Inequality, Continuity and Change. He blogs at Inequality by (Interior) Design, where this post originally appeared. You can follow Dr. Bridges on Twitter.