Recently there’s been heightened attention to calling out microaggressions and giving trigger warnings. I recently speculated that the loudest voices making these demands come from people in categories that have gained in power but are still not dominant, notably women at elite universities. What they’re saying in part is, “We don’t have to take this shit anymore.” Or as Bradley Campbell and Jason Manning put it in a recently in The Chronicle:
…offenses against historically disadvantaged social groups have become more taboo precisely because different groups are now more equal than in the past.
It’s nice to have one’s hunches seconded by scholars who have given the issue much more thought.
Campbell and Manning make the context even broader. The new “plague of hypersensitivity” (as sociologist Todd Gitlin called it) isn’t just about a shift in power, but a wider cultural transformation from a “culture of dignity” to a “culture of victimhood.” More specifically, the aspect of culture they are talking about is social control. How do you get other people to stop doing things you don’t want them to do – or not do them in the first place?
In a “culture of honor,” you take direct action against the offender. Where you stand in society – the rights and privileges that others accord you – is all about personal reputation (at least for men). “One must respond aggressively to insults, aggressions, and challenges or lose honor.” The culture of honor arises where the state is weak or is concerned with justice only for some (the elite). So the person whose reputation and honor are at stake must rely on his own devices (devices like duelling pistols). Or in his pursuit of personal justice, he may enlist the aid of kin or a personalized state-substitute like Don Corleone.
In more evolved societies with a more extensive state, honor gives way to “dignity.”
The prevailing culture in the modern West is one whose moral code is nearly the exact opposite of that of an honor culture. Rather than honor, a status based primarily on public opinion, people are said to have dignity, a kind of inherent worth that cannot be alienated by others. Dignity exists independently of what others think, so a culture of dignity is one in which public reputation is less important. Insults might provoke offense, but they no longer have the same importance as a way of establishing or destroying a reputation for bravery. It is even commendable to have “thick skin” that allows one to shrug off slights and even serious insults, and in a dignity-based society parents might teach children some version of “sticks and stones may break my bones, but words will never hurt me” – an idea that would be alien in a culture of honor.
The new “culture of victimhood” has a different goal – cultural change. Culture is, after all, a set of ideas that is shared, usually so widely shared as to be taken for granted. The microaggression debate is about insult, and one of the crucial cultural ideas at stake is how the insulted person should react. In the culture of honor, he must seek personal retribution. In doing so, of course, he is admitting that the insult did in fact sting. The culture of dignity also focuses on the character of offended people, but here they must pretend that the insult had no personal impact. They must maintain a Jackie-Robinson-like stoicism even in the face of gross insults and hope that others will rise to their defense. For smaller insults, say Campbell and Manning, the dignity culture “would likely counsel either confronting the offender directly to discuss the issue,” which still keeps things at a personal level, “or better yet, ignoring the remarks altogether.”
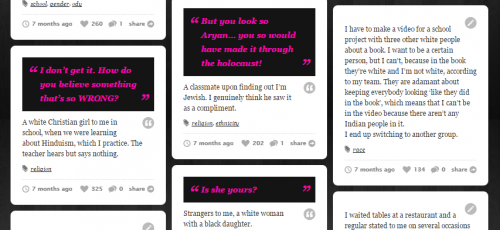
In the culture of victimhood, the victim’s goal is to make the personal political. “It’s not just about me…” Victims and their supporters are moral entrepreneurs. They want to change the norms so that insults and injustices once deemed minor are now seen as deviant. They want to define deviance up. That, for example, is the primary point of efforts like the Microaggressions Project, which describes microaggressions in exactly these terms, saying that microaggression “reminds us of the ways in which we and people like us continue to be excluded and oppressed” (my emphasis).
So, what we are seeing may be a conflict between two cultures of social control: dignity and victimhood. It’s not clear how it will develop. I would expect that those who enjoy the benefits of the status quo and none of its drawbacks will be most likely to resist the change demanded by a culture of victimhood. It may depend on whether shifts in the distribution of social power continue to give previously more marginalized groups a louder and louder voice.
Cross-posted at Montclair SocioBlog.
Jay Livingston is the chair of the Sociology Department at Montclair State University. You can follow him at Montclair SocioBlog or on Twitter.