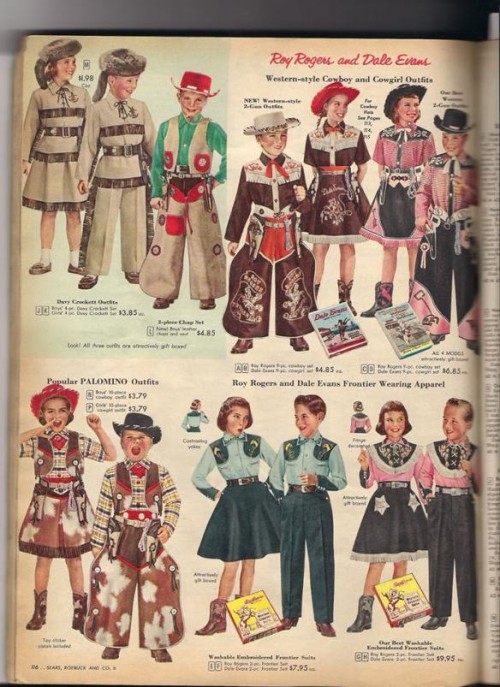
We’re celebrating the end of the year with our most popular posts from 2013, plus a few of our favorites tossed in. Enjoy!
@bfwriter tweeted us a link to a college design student’s photograph that has gone viral. Rosea Lake posted the image to her tumblr and it struck a chord.
What I like about the image is the way it very clearly illustrates two things. First, it reveals that doing femininity doesn’t mean obeying a single, simple rule. Instead, it’s about occupying and traveling within a certain space. In this case, usually between “proper” and “flirty.” Women have to constantly figure out where in that space they’re supposed to be. Too flirty at work mean’s you won’t be taken seriously; too proper at the bar and you’re invisible. Under the right circumstances (e.g., Halloween, a funeral), you can do “cheeky” or “old fashioned.”
The second thing I like about this image is the way it shows that there is a significant price to pay for getting it wrong. It’s not just a faux pas. Once you’re “‘asking for it,” you could be a target. And, once you’re reached “prudish,” you’ve become socially irrelevant. Both violence and social marginalization are serious consequences.
And, of course, all women are going to get it wrong sometimes because the boundaries are moving targets and in the eye of the beholder. What’s cheeky in one setting or to one person is flirty in or to another. So women constantly risk getting it wrong, or getting it wrong to someone. So the consequences are always floating out there, worrying us, and sending us to the mall.
Indeed, this is why women have so many clothes! We need an all-purpose black skirt that does old fashioned, another one to do proper, and a third to do flirty… at the very least… and all in casual, business, and formal. And we need heels to go with each (stilettos = provocative, high heels = flirty, low heels = proper, etc, plus we need flats for the picnics and beach weddings etc). And we need pants that are hemmed to the right length for each of these pairs of shoes. You can’t wear black shoes with navy pants, so you’ll need to double up on all these things if you want any variety in your wardrobe. I could go on, but you get the picture.
Women’s closets are often mocked as a form of self-indulgence, shop-a-holicism, or narcissism. But this isn’t fair. Instead, if a woman is class-privileged enough, they reflect an (often unarticulated) understanding of just how complicated the rules are. If they’re not class-privileged enough, they can’t follow the rules and are punished for being, for example, “trashy” or “unprofessional.” It’s a difficult job that we impose on women and we’re all too often damned-if-we-do and damned-if-we-don’t.
Cross-posted at Business Insider and The Huffington Post; view the original.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.