For the last week of December, we’re re-posting some of our favorite posts from 2012.
In Counted Out: Same-Sex Relations and Americans’ Definitions of Family, released last month, authors Brian Powell, Catherine Bolzendahl, Claudia Geist, and Lala Carr Steelman look at how Americans conceptualize “the family” — that is, not what they think about their own families, but what they think counts as a family. Which groups or living arrangements do they include in the definition of “family,” and who is excluded?
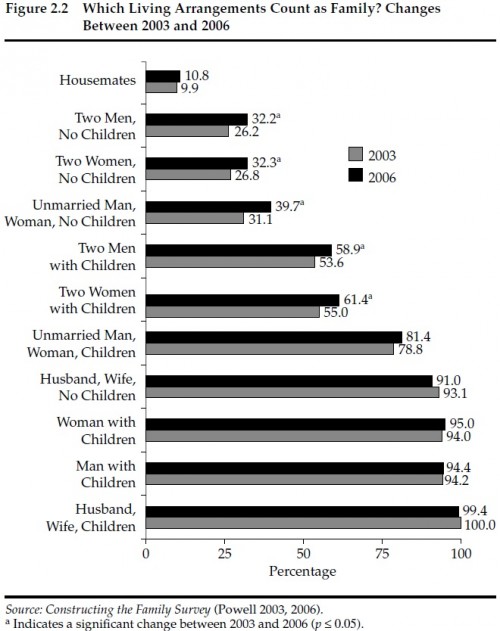
Based on surveys conducted in 2003 and 2006, Americans still hold the stereotypical nuclear family (husband, wife, kids) as the gold standard — virtually everyone agrees that such a group counts as a family. Being legally married, or the presence of children, generally leads to acceptance of a grouping as a family — the overwhelming majority believed single parents and their children count as families, as do married heterosexual couples without kids, and even unmarried heterosexual couples who have children. But when couples are same-sex, or don’t have kids, Americans are much less certain that they can qualify as a family. In 2006, the percent of respondents believing gay or lesbian couples with kids are families was notably smaller than for those agreeing that single parents or straight couples count, though it had increased since 2003:
And notice the importance of children to definitions of family — only a minority of respondents thought that gay, lesbian, or straight couples without kids are a family.
The authors divided respondents into three groups, based on their answers: exclusionists (those with the most restrictive definitions of family), moderates, and inclusionists (those with the most expansive definitions). Looking at the words these groups used as the talked about their characterizations of family, we see clear differences. The words used most frequently by exclusionists highlight the centrality of marriage, as well as an emphasis on what type of people constitute a family (husband, wife, woman, man), and the explicit inclusion of religious-based elements in their ideas of what makes a family:
The language used by inclusionists emphasized emotional attachments rather than the legal institution of marriage as the basis for determining what counts as a family:
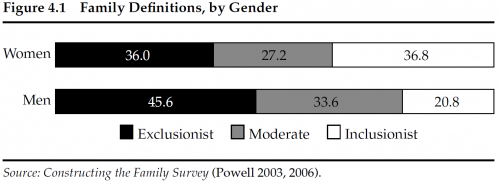
Women were more inclusive than men, in general:
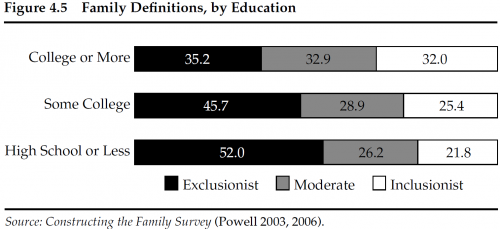
The more educated respondents were, the more inclusive their definitions of family tended to be:
The Russell Sage Foundation released these and many other charts and tables from the book, so it’s definitely worth a look if you’re interested in how Americans think about the family. Overall, the authors found that definitions of the family were becoming more inclusive. Presumably this trend has continued and even accelerated since the 2006 survey, given how attitudes have shifted on a number of issues involving gay and lesbian rights in the past few years.
Gwen Sharp is an associate professor of sociology at Nevada State College. You can follow her on Twitter at @gwensharpnv.


Comments 70
pduggie — July 18, 2012
So as support for gay relationships has grown, there has been a similar growth in those willing to identify an unmarried hetero couple as a 'family'. And an actual small drop in people identifying a married herteo couple with kids as a family O_o
Sounds to me like evidence that something is undermining marriage....
David M Pickett — July 18, 2012
Now that same sex marriage is legal in a number of states, I hope that they add categories like: "Husband, Husband" "Wife, Wife" "Husband, Husband, Children" and "Wife, Wife, Children" to distinguish between married and unmarried LGBT couples. I'm curious to see if there's a discernible difference there
hopeless shade — July 18, 2012
I admire the transcriber who accounted for all of those uhs and ums.
Croquis — July 18, 2012
This is such an interesting study. The word 'family' is so charged in the military culture as meaning wife, husband, child (I think I mentioned before how my partner was denied 'family time' off because we are not a family, according to them) So I'm glad that more people are seeing the value of all different kinds of families. I do think the wording is confusing- 2 women, in the same apartment, are they a family? I don't know; what do they call each other?
hypatia arez — July 18, 2012
I find it depressing how much paper still matters. A fifty point difference between cohabitating and married heterosexual couples.
Vadim McNab — July 19, 2012
Sounds about right to me.
Patti — July 19, 2012
I am intrigued to know of the 0.6% who did not call the husband wife kids scenario a family, did any of them not include anything as a family, and if they did, then what counted as a family to them.
Barney — July 19, 2012
Was there an option for 'family' is a fuzzy concept that means a range of things dependent on context and it is not always possible to neatly categorize any group of people as either family or not a family?
NancyP — July 19, 2012
Life must be hell for the involuntarily infertile heterosexual married couples, especially the women, in exclusionary communities.* They are doing all the "right" things but are still pariahs, "not a family", recipient of pity and condescension. One hopes that they would take the hint and leave the jerks behind.
* yes, hell for LOTS of non-normative people in those communities. Women who don't marry early, men who don't marry at the accepted time or who marry "unacceptable" women, slightly femme-sounding heterosexual men, heterosexual men who have non-macho interests, and....we haven't even gotten close to the long list of "unacceptable" LGBTQIA people.
Antonia — July 19, 2012
This might be addressed in the PDF, but I couldn't find it there: I'm assuming that the "Two Women, Two Men" and so forth situations for unmarried people only include couples, and that this was made clear in the original survey? If not, that data does not mean what you think it means.
Tinkerballa — July 19, 2012
I don't know about being an "exclusionist", but my definition of family is pretty straight forward. If the Family Pass at Six Flags saves you money than buying individual tickets, then you're a family.
HOW DO WE DEFINE A FAMILY? « Welcome to the Doctor's Office — July 21, 2012
[...] from SocImages [...]
Second Degree Susan — July 22, 2012
[...] The first was a graph that accompanied an article by Gwen Sharp titled “How Do We Define a Family?” [...]
Amy — August 12, 2012
As a woman with two husbands and four children in one household, apparently we don't exist - families with more than two adults aren't even included in the possible definitions of family. Very disappointing. And we ARE family, regardless of what other Americans say.
guest — September 2, 2012
what about a man and 2 women or 2 men and a woman?
why was this study exclusionist?
KayG — January 8, 2013
I find it very interesting that "the more educated respondents were, the more inclusive their definitions of family tended to be." I wonder which elements in the education process could have caused this shift in thought; for example associated experiences, environment, knowledge, etc.
Classroom Bookshelf Beta - Red Thread Sisters — March 27, 2013
[...] http://thesocietypages.org/socimages/2012/12/26/how-do-we-define-a-family/ [...]
2.5 Kids and a Dog | TTC — August 8, 2014
[…] How Do We Define a Family?This article looks at a survey asking Americans if they define themselves as a family. – What […]
dịch vụ seo - đào tạo seo không backlink — May 28, 2020
Hi, I wish for to subscribe for this webpage to get newest updates,
therefore where can i do it please assist.