Abortion is highly politicized in the U.S. (more so than in many other countries) and the fight between those who are in favor of and against available abortion occurs on two fronts. One is familiar to just about everyone: the effort to overturn Roe v. Wade, the legislation Supreme Court decision that established the legality of abortion in 1973.
The second front, though, is less familiar. It involves reducing the ease of access to legal abortion. Efforts to increase barriers to accessing legal abortion include passing laws that require minors to notify their parents of an abortion or get their consent, requiring mandatory counseling for abortion-seekers, instituting waiting periods, and discouraging medical schools from teaching abortion procedures. Some of the issues of diminishing access are non-movement related; others are the direct result of pro-life activism.
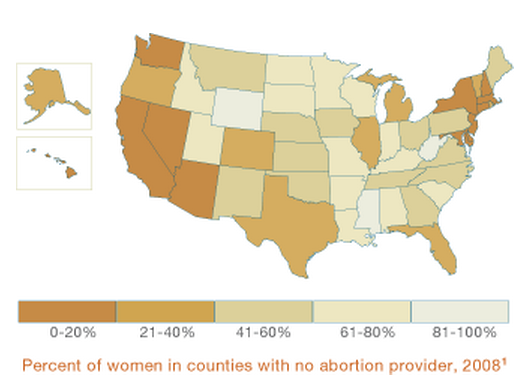
I bring this up in order to focus on an additional barrier to access: a reduction in the number of clinics and hospitals that provide abortions. The map below, based on data from the Guttmacher Institute and compiled by ANSIRH, shows how availability varies by state. In the darkest states, up to 20% of women live in a county with no abortion provider; in the lightest states, between 81 and 100% percent do.
Living far from the nearest abortion provider is a problem especially for low-income women. Such women are less likely to have an employer who will give her a day off to travel to the clinic, less likely to get a paid sick day, and less likely to be able to afford to lose even a single day’s wages. She is also less likely to have a car, making it more difficult to get to a distant location, and less likely to have reliable day care for any existing children. If the state requires in-person counseling and has a waiting period, it means that the woman must take two days off, travel to and from the clinic twice, and arrange for child care on multiple days.
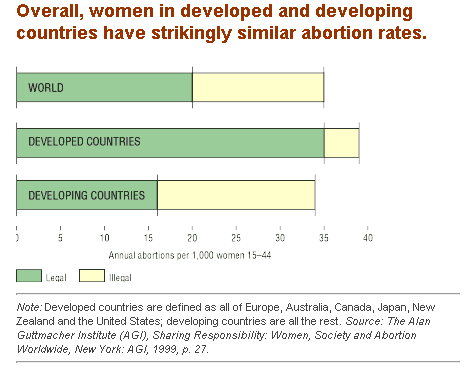
Reduction in the availability of abortion does not necessarily reduce the number of abortions. We recently posted global data showing that less liberal abortion laws actually correlate with higher rates of abortion. The data below, also from Guttmacher, show that were abortion laws are less liberal (largely in developing countries), the rate of abortion is 34/1,000 women oer year, compared to 39/1,000 in developed countries (the difference may look significant here, but imagine how trivial it would look if the horizontal axis went all the way to it’s true maximum of 1,000):
Guttmacher explains that the relevant variable isn’t availability of abortion, but the unintended pregnancy rate (which is surprisingly high in the U.S.).
Barriers to accessing abortion, then, don’t lower the abortion rate. They do, however, increase the likelihood that an abortion procedure will occur later in pregnancy and guarantee a greater logistic burden on the pregnant woman.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.
Comments 22
Anonymous — April 24, 2012
(the difference may look significant here, but imagine how trivial it would look if the horizontal axis went all the way to it’s true maximum of 1,000)
1000 abortions / 1000 women / yr is not the "true maximum" of the axis. On one side, it's biologically possible (but probably extremely unhealthy) for an individual woman to have more than one abortion in a year; on the other side, infertile women (including those post-menupausal) cannot get an abortion.
The better scale length for nondimensionalization would probably be the number of live births per 1000 women, although it would vary on a country-by-country basis.
ACCESS TO ABORTION CLINICS AND THE ABORTION RATE « Welcome to the Doctor's Office — April 24, 2012
[...] from SocImages [...]
Kelsey — April 24, 2012
Oh Wyoming, not so much the equality state anymore, eh?
Miranda Loeber — April 24, 2012
I think using living in a county with an abortion provider as a measure is a mistake. Counties are all different sizes, and different states have different numbers and sizes of counties. Arizona is a very conservative state, as most people know, so it was weird that it was one of the darkest - but it also has very large counties, and only 15 of them. Mississippi, on the other hand, one of the lightest states, is about a third the size of Arizona but has 82 very small counties. It's not surprising that so many women live in a county with no abortion provider when the counties are so small. How about measuring distance from an abortion provider instead?
Law Person — April 24, 2012
A minor nit to pick: Roe v. Wade was a decision of the Supreme Court. It is not legislation.
Abortion Depictions in Pop Culture: Why “Reproduction and Abortion Week” At ‘Bitch Flicks’ Is So Crucial | The Opinioness of the World — April 25, 2012
[...] Increasing barriers to abortion do not reduce the abortion rate. Instead, abortion access barriers increase abortion rates, especially those occurring in later terms. As abortion costs also increase the later in pregnancy the later they are performed, it places a greater financial burden on those seeking abortions, particularly those who are low-income, people of color and queer communities – “queer people of color, in particular, are disproportionately economically disadvantaged when it comes to mortgages, wages, and staying above the poverty line.” [...]
Abortion Depictions in Pop Culture: Why Bitch Flicks’ Reproduction & Abortion Week Matters — April 29, 2012
[...] Increasing barriers to abortion do not reduce the abortion rate. Instead, abortion access barriers increase abortion rates, especially those occurring in later terms. As abortion costs also increase the later in pregnancy the later they are performed, it places a greater financial burden on those seeking abortions, particularly those who are low-income, people of color and queer communities – “queer people of color, in particular, are disproportionately economically disadvantaged when it comes to mortgages, wages, and staying above the poverty line.” [...]
machineflesh, bioart & life support | thestate — May 8, 2012
[...] some discussion, but—as seems to be the standard with both bioart and debates over stem cells and abortion, never [...]