Rachel sent in a link to a post about the recession by Tim Cavanaugh at Reason that led me to an interactive graphic at the Wall Street Journal that lets you track job loss by either sector or by race/ethnicity and sex from December 2007 to August 2010.
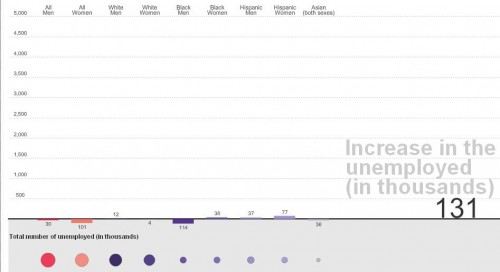
Here is the race/ethnicity and sex data for January 2008 (for reasons I cannot understand, Asians are not separated out by sex, and as usual, American Indians aren’t included):
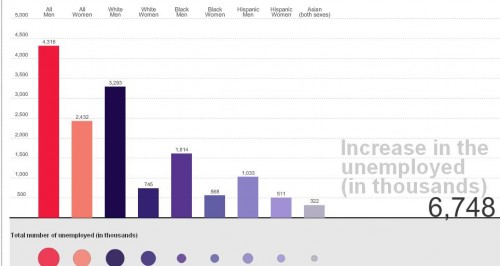
And here’s the breakdown for January 2010:
Unfortunately, the numbers aren’t weighted by the number of total workers per category, so we don’t have any way to know how these raw numbers translate into percentages of workers losing their jobs.
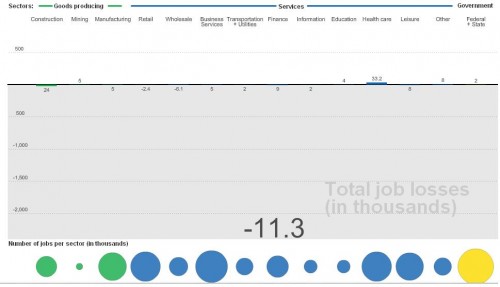
By economic sector, for January ’08:
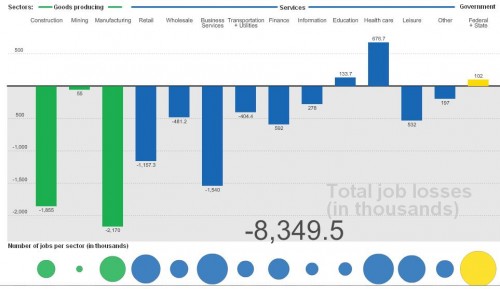
January ’10:
[On a nitpicky note, the sector graphs show job losses in negative numbers, which would work if it showed total change in # of jobs. But I think we’d be thrilled if we had -8… thousand job losses, as the graph is labeled. Just a small sloppy labeling issue.]
As the data show, and as we’ve discussed before, the economic recession has disproportionately affected men. But Cavanaugh cautions that it might be a little soon to declare men an at-risk species or lament the bad luck of being born male. Presumably, if men’s over-representation in construction, for instance, has meant they suffered more than women from the real estate bust, if you felt like it you could turn it around and argue that perhaps they disproportionately benefited from the boom that preceded it. Additionally the employment sectors are pretty broad; “retail” or “finance” will include some specific occupations that are fairly gender balanced, some that are dominated by men, and some dominated by women. And overall loss in retail jobs doesn’t tell us if the losses are spread equally across occupations within the sector.
Should we care about the suffering of men and their families in the recession? Of course. And to the degree that men are disproportionately represented in occupations that are prone to boom/bust cycles, we’re likely to continue to see greater volatility in their employment rates than women’s, sometimes to their advantage, sometimes not. But we might want to be a little careful and look at some more in-depth data before we declare, as some commentators seem to want to do, that women have basically escaped the recession. If nothing else, men and women aren’t islands; lots of us share household expenses, and a woman whose husband loses his job but keeps her own doesn’t exactly avoid any negative consequences of the recession.
Related posts: more comparisons of joblessness, race and recession, unemployment and education level, not everyone suffers during a recession, the gender employment gap,

Comments 2
Sam — September 13, 2010
I would also wonder how many women compared to men might be in fields where they're keeping their jobs but seeing their hours cut back to below what can provide a minimum standard of living (I'm thinking waitressing, cashiering, etc.)
Sungold — September 13, 2010
Wonderful post, and perfect timing! I'll use this in my intro to Women's and Gender Studies class this week, where we'll be talking about intersectionality. I'm hopeful it might help them understand how precarious black men's position is, for instance, in our purportedly "post-racial society." (As if!!)