Dr. Paul Baker, a linguist at the University of Lancaster, sent us some graphs from his analysis of use of gendered language over time in the U.K. His data consisted of “four sets of data from written British English from 1931, 1961, 1991 and 2006 (a million words each)” — a full discussion of the methodology will be available in the forthcoming article in Gender and Language.*
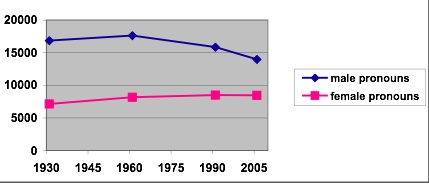
First, Dr. Baker looked at use of male and female pronouns (he/his/him vs. she/hers/her) over time:
Clearly male pronouns are still used more than female ones, but the gap is narrowing. Baker found that though part of the reason is that male pronouns are more likely to be used generically to refer to everyone than female pronouns are, the major reason is that men are discussed more than women.
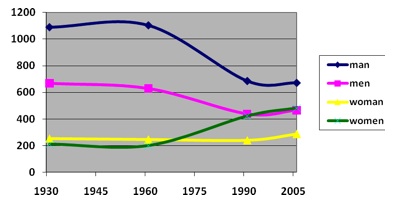
Here are the data specifically for the four words “man,” “men,” “woman,” and “women”:
Notice that the use of the plurals — “men”and “women” — have converged, though we still see higher usage of the male singular than of “woman.”
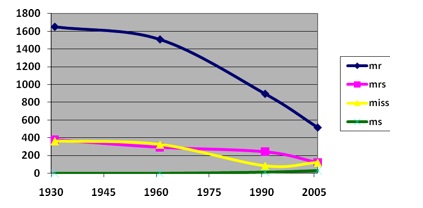
And finally, Dr. Baker looked at the usage of four gendered titles:
A large decrease, obviously, especially in the use of “Mr.,” but all have tapered off since the 1930s with the exception of “Ms.,” which never did really catch on. Baker argues that while some of the decrease may be due to attempts to use less sexist language, it’s more likely because of more informalization of society in general — titles of address often seem stiff and overly formal today.
Of course, this analysis just tells us the frequency with which these terms are used, not what is actually being said about men and women, a topic he addresses in the full article. But he concludes that the trend is rather encouraging for those who want to see more equal gender representation in terms of language.
* Baker, P. (2010) ‘Will Ms ever be as frequent as Mr? A corpus-based comparison of gendered terms across four diachronic corpora of British English.’ Gender and Language. Forthcoming.

Comments 55
Jen — September 12, 2010
It is startling for me to see (in the second chart) how little women are discussed as individual beings in comparison to men. The tendency seems to be to speak about women as a homogenous group while men are spoken about and regarded as individuals. I hope to see a greater shift in the future toward addressing the individual woman rather than regarding her as part of a collective femininity.
finette — September 12, 2010
Well, "man" is also used as a generic for the human race, more frequently than we might realize: "one small step for man," "man's inhumanity to man," etc.
T — September 12, 2010
What does "Ms never really caught on" mean? I'm not contesting the numbers... but what other title is there? I use Ms. all of the time when referring to a woman (not otherwise title) by last name.
Other than military, religious and certain academic titles, I only know of three: Mr, Ms and Dr.
If Dr. doesn't apply, then you use Mr. or Ms.
What else is there? Am I missing something?
Umlud — September 12, 2010
I'm going to run the same words through the Corpus of Historical American English, and see what comes up.
eeka — September 13, 2010
The words "Mr." and "Ms." and whatnot need to stop existing at all. We need to come up with a way to show respect and formality without needing to label gender. Come to think of it, we don't, since body language and word choice and whatnot convey formality and respect just fine. Let's lose the antiquated gendered sexist terms.
Lance — September 13, 2010
I know that the article is still forthcoming, but it would be extremely useful in evaluating this data to know exactly which "written British English" Baker was using. Novels? Personal letters? The Times? The Sun? For instance, if the written British English that Baker is using is the political reporting from the Times of London, I'd hardly be surprised that it's still the case that more men than women are discussed. That wouldn't be a fact about "gendered language", it would be a fact about the British political system.
In fact, in general, I very much wonder whether the results are telling us anything about gender and language, as opposed to gender and the domains in which the written speech was examined. Which is, of course, all the more reason to look at the full article.
rebecca — September 13, 2010
Um... Didn't anyone think to add up the frequencies of Ms., Mrs., and Miss? Wouldn't that make more sense, seeing as there is only one title to refer specifically to males? Obviously feminine titles are going to individually be less frequent if there are more of them.
Niki — September 14, 2010
"Notice that the use of the plurals — 'men' and 'women' — have converged, though we still see higher usage of the male singular than of 'woman.' "
I did notice that - and I also noticed something else weird about that graph. It seems that "Man," the singular, is used more frequently than "men," the plural. But "Women," the plural, is more frequent than "woman," the singular.
So why might that be? Is that patriarchy rearing its head - do we have a tendency to refer to women as a collective, while with men we emphasize the originality? Is this also related to the frequency with which "man" is used to refer to the human race?
Gays on TV, Women in The Men’s Room and Bad Behavior at Goldman Sachs: Editors’ Picks, 9/12-9/18 : Ms Magazine Blog — September 17, 2010
[...] Research from linguist Dr. Paul Baker on changes in the use of gendered language over time indicates that, slowly, we are headed in the right direction. Check out the data at Sociological Images. [...]