Picture of the week comes from David Banks. FourSquare and Occupy at that critical intersection of the digital and physical.
This week at Cyborgology…
Picture of the week comes from David Banks. FourSquare and Occupy at that critical intersection of the digital and physical.
This week at Cyborgology…
On this blog we talk a lot about “augmented reality,” or how the digital and the material are increasingly mutually constitutive. As an example of this concept, I bring you the following development: Britain’s ‘Safe Text’ Street.

There are many theories that seek to clarify the relationship between our offline existence and whatever it is we are doing online. I say “whatever” not to be flippant, but because there is a great deal of debate about the ontological, conceptual,and hermeneutic ramifications of online activity. How much of ourselves is represented in our Skyrim characters? Is retweeting an #ows rally location a political act? How is access to the Internet related to free speech? These are questions that some of the greatest minds of our day are contemplating. I know some equally smart people that would throw up their hands in frustration at even considering these topics as worthy of research and critical analysis. Regardless of whether or not you think it is worth pondering these questions, people all over the world are engaging in something when they post a Facebook status or check in to a coffee shop on Foursquare. In his Defending and Clarifying the Term Augmented Reality, Nathan described how our relationship to these sorts of digital Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) fits in with our historial relationship to technology: “technology has always augmented reality, be it in pre-electronic times (e.g., architecture or language as technologies) or how those offline are still impacted by the online (e.g., third-world victims of our e-waste or the fact that your Facebook presence influences your behavior even when logged off).” I have argued elsewhere that, even if ICTs mark a fundamental shift in our relationship to technology, it is only another wave in a constantly evolving relationship to our own understanding of technological progress. I am going through this (hyperlinked) summary of many of this blog’s larger arguments because 1) we have been growing in readership, and 2) we are embarking on a new, ongoing, project to situate Augmented Reality (AR) amongst other theories of society’s relationship to technology. Today I want to introduce Actor Network Theory (ANT). more...
It’s a notable coincidence that Steve Job died exactly two decades after Neil Stephenson completed Snowcrash, arguably, the last great Cyberpunk novel. Stephenson and Jobs’ work exemplified two alternative visions of humans’ relationship with technology in the Digital Age. Snowcrash offers a gritty, dystopian vision of a world where technology works against human progress as much as it works on behalf of it. Strong individuals must assert themselves against technological slavery, though ironically, they rely on technology and their technological prowess to do so.
Apple, on the other hand, tells us that the future is now, offering lifestyle devices that are slick (some might say, sterile). Despite being mass produced, these devices are supposed to bolster our individuality by communicating our superior aesthetic standards. Above all, Apple offers a world where technology is user-friendly and requires little technical competency. We need not liberate ourselves from technology; there’s an app for that.
Values and style are inextricably linked (as Marshal McLuhan famously preached). So, unsurprisingly, the differences between Apple’s view of the future and that of Cyberpunk authors such as Stephenson run far deeper. The Cyberpunk genre has a critical mood that is antithetical to Apple’s mission of pushing its products into the hands of as many consumers as possible. The clean, minimalist styling of Apple devices makes a superficial statement about the progressive nature of the company, while the intuitive interface makes us feel that Apple had us in mind when designing the product—that human experience is valued, that they care. Of course, this is all a gimmick. Apple invokes style to “enchant” its products with an aura of mystery and wonderment while simultaneously deflecting questions about how the thing actually works (as discussed in Nathan Jurgenson & Zeynep Tufekci’s recent “Digital Dialogue” presentation on the iPad). Apple isn’t selling a product, it’s selling an illusion. And to enjoy it (as I described in a recent essay), we must suspend disbelief and simply trust in the”Mac Geniuses”—just as we must allow ourselves to believe in an illusionist if we hope to enjoy a magic show. Thus, the values coded into Apple products are passivity and consumerism; it is at this level where it is most distinct from the Cyberpunk movement. more...
Facebook Inc. and researchers from the University of Milan recently released a study showing that Facebook users are linked by only 4.7 degrees of separation. This is a significant decrease from the 6 degrees of separation found in Milgrim’s 1967 study, from which the common conception of our degree of networked connection (and the Kevin Bacon game) stems.
Here, I examine what these findings mean in terms of social relationships in the contemporary era.
These findings point to three main things: In the most basic sense, these findings show that Facebook is a highly pervasive and global platform through which interaction takes place. Relatedly, those who interact on Facebook connect to large and diverse networks. Finally, as we increasingly interact on a shared platform, with a wide and diverse group of others, these findings indicate that we are increasingly connected through weak ties. It is this last point that I will expand upon more...
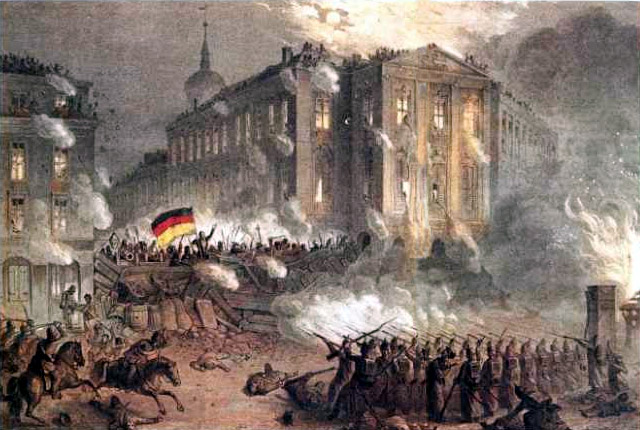
With all the rhetoric around “Facebook Revolutions” and “Twitter Revolutions”1 that we’ve had to endure over the last couple of years, it’s easy to get the sense that there’s something new about the character of contemporary political protest and revolutionary action, and that this newness is, in some fundamental way, the practical result of the omnipresent nature of technology. It’s difficult to miss the profound interweaving and enmeshing of the physical and digital aspects of protest as we see it in both the Arab Spring and Occupy Wall Street – the weight of the protests produced by the occupation of physical space by gathered human bodies, coupled with the constant documentation and nearly instantaneous sharing of images, video, and text that have chronicled these physical occupations and arguably helped them to grow – in short, the augmented nature of contemporary social action. We see this and to us it feels new. Even if we recognize that there are old things at work here – symbolism, patterns of mobilization and diffusion, pieces of the past reclaimed for the purpose of the present – we at least feel instinctively that there is something novel about the Arab Spring, Occupy, and all the other movements and events that have birthed themselves in correlation.

After the many, many evictions which have taken place over the last several weeks, both here in Canada and in the United States, there has been a lot of discussion about the ‘next phase’ of the Occupy movement. My personal interest has been focused, from the start, on the specific instance of the New York occupation, so it is their eviction and current situation which interests me the most. I specify this up front because I think it is difficult to speak about the OWS movement as a Whole in meaningful terms, since each occupation is so localized. I like the comparison to open-source projects for this: some useful generalizations are possible, but the source code is open to tinkering and adapted to each specific use.
Recently, the NY Occupation was evicted from their previous home at Liberty park, and scattered to the four winds. They have so far proven that they have the institutional robustness to deal with this by continuing to provide food and shelter to all in need, as well as continuing to effectively plan and implement direct actions along with effective media. They have even continued their regularly scheduled General Assemblies and Spokes Councils, despite cold weather, a hard time finding space, and what seem to be increasing feelings of tension amongst certain committed members.
I see this continued ability to act as centrally linked to their being an Augmented Movement. Because they represent this blend of atoms and bits they have been able to continue coordinating effectively by transferring ever more of that coordination online. However, as an augmented movement, they face unique problems. Bits are well and good, but atoms are tricky things, and certain things can only continue to happen offline: people need food and places to stay, as well as the need to meet and communicate face to face so that strong links can be maintained along with the horizontal institutions upon which the current movement is premised. It is this second aspect of their problem which I find most interesting, and challenging. more...
I wanted the photo above to be an example of the new so-called “living pictures” that have garnered much recent attention. However, Lytro has not provided proper embedding code so I can only post this screenshot of a living photo. I highly recommend clicking on the photo or clicking here before reading along.
Update: the code now works, so before reading on, click the photo above. Click around various parts of the image and watch the focus change.
Okay, by now you have experienced a living photo. You see it, but you can also make it come alive; touch it, change the focus, reorient what is seen and focused on. Some might even argue that you get to decide the meaning of the story the image tells. This post asks: what would it mean if we start posting living pictures across social media? Might it change how we take photos? How might we differently interact with social media photography when we can manipulate the faces of our friends and engage with the images in a new way?
It has been my contention that photography can teach us quite a bit about social media. Not just because there are so many photos online but because photography serves as a familiar and grounding reference point to the newness of social media. Photography situates the novel and sometimes disorienting ways we are documenting ourselves online with a technology that did the same offline more than a century ago.
I have written about Susan Sontag’s description of photographers being always at once poets and scribes when taking photos to describe how we create our social media profiles in a similar way. I have used the concept of the “camera eye” photographers develop to discuss how social media has imbued us with a similar “documentary vision.” I also described how the explosion of faux-vintage photos taken with Hipstamatic and Instagram serve as a powerful example of how social media has trained us to be nostalgic for the present in a grasp at authenticity.
Here, I want to discuss what many are calling “revolutionary” and the next “big thing” in photography: the so-called living pictures linked to above developed by the Lytro company that have just entered the consumer market with cameras shipping early next year.
Lytro “Living Picture” Technology
This is not an essay so much about the technology but instead the implications of more...
 Photo of the week comes from the current protests in Egypt. The picture captures the flow of imagery across mediums, especially in times of protest. Al Jazeera ran the photo of a police officer who reportedly is shooting protesters in the eye. Infuriated, Egyptians stenciled his image on walls. The graffiti was then photographed and disseminated on social media, where Zeynep Tufekci saw the image and sent it to us. The image of the police officer flows from cameras to TV broadcast to paint on walls back into photo-form into social media and onto this blog where you see it now. Reality is augmented.
Photo of the week comes from the current protests in Egypt. The picture captures the flow of imagery across mediums, especially in times of protest. Al Jazeera ran the photo of a police officer who reportedly is shooting protesters in the eye. Infuriated, Egyptians stenciled his image on walls. The graffiti was then photographed and disseminated on social media, where Zeynep Tufekci saw the image and sent it to us. The image of the police officer flows from cameras to TV broadcast to paint on walls back into photo-form into social media and onto this blog where you see it now. Reality is augmented.
Meanwhile, this week on Cyborgology…
Jenny Davis writes about the mileage Facebook critics get out of misusing the word “friend”
David Banks gets into the Thanksgiving spirit and discusses sexism and Internet food videos
And we round up this week with the second part of Dan Greene’s “augmented syllabus” project
In this space, about a month and a half ago, I laid out my design and pedagogy strategies for my mixed online/in-person AMST 201: Introduction to American Studies course. These strategies all hinged on the core idea of a building an augmented syllabus for an augmented reality: Web-based, in-class, and other tools each have their own strengths and weaknesses which can support or hamper learning objectives. In order to help students apply new ideas to their everyday lives, I’ve tried to
For the most part, there hasn’t been much student pushback and class is going well. Midterm exam grades were above average, and student responses to my midterm feedback form—which included technology-focused questions—were generally positive. That feedback is crucial, not just self-check data but a way to keep emphasizing the importance of transparency to the learning process. Keeping my core ideas and strategies in mind, I want to draw from student feedback and my own observations and experiences to review what’s worked so far, what hasn’t, and what can change. more...